
What is biotechnology?
April 16, 2025

- Related Topics:
- Bioinformatics,
- Biotechnology,
- Genetic engineering,
- Genomics
A high school student from Pennsylvania asks:
"What is biotechnology?"
Biotechnology: technology using biology. While that may seem simple, biotechnology is a complex field that continues to change with new discoveries. Let’s explore more about what biotechnology is and a few examples of how it is changing our world.
Biotechnology Overview
Biotechnology is a field of science that describes the use of biological systems to develop products and technologies. Just like a sports team works together to accomplish something, like scoring points in a basketball game, a biological system includes different parts working together to do a job. For example, the human body is a biological system where organs work together to accomplish the job of keeping us alive.
Biotechnology in History
Humans have been harnessing the power of living organisms and their natural systems for centuries. For example, yeast is a fungus that undergoes the biological process of fermentation, which converts sugar molecules to a gas (carbon dioxide). We use yeast and the fermentation process to bake bread since the gas it creates gets trapped within the dough, causing it to rise.
Other examples of biotechnology throughout history include the selective breeding of plants and animals in agriculture. Since humans learned that offspring can inherit traits from their parents, they’ve made organisms with desired traits by selecting which parent organisms to breed. For example, if a farmer found that a certain cow produced more milk than other cows, they might selectively use that cow for breeding so that they would get offspring that produced more milk, too.
In addition to baking and agriculture, biotechnology has played a pivotal role in the history of medicine development. For example, the biological process by which microbes (tiny living organisms that are too small to be seen by the eye, like bacteria, viruses, and fungi) kill other microbes has been harnessed in antibiotics to help fight disease.
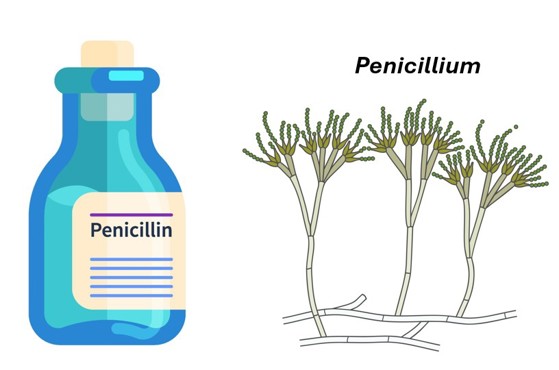
While humans have been using the natural power of biological systems throughout history, new scientific discoveries are creating new ways for biotechnology to change our world.
Bugs Be Gone! Biotechnology in Plants
While historical breeding processes have improved the production of crops and livestock through selecting for desired traits, genetic engineering has revolutionized agriculture. Genetic engineering is the use of laboratory techniques to change the genetic makeup of a plant or animal. Since an organism's genetic makeup–its genes and DNA–determines its traits, genetic engineering can be used to change DNA and genes to produce a desired trait. Because genetic engineering uses genetic biological systems to create a product, like a crop, genetic engineering is a form of biotechnology.
A few major challenges face crop producers, particularly the weeds, diseases, and insects that threaten plant health. Additionally, the tools used to fight these pests can harm the crops, the health of the soil, or the consumers of the crop products. Genetic engineering is being utilized to combat these problems. For example, there are cotton crops that have been genetically engineered to be insect-resistant. This prevents the need for chemicals to kill the insects, which can contaminate the groundwater and environment.

Genetic Editing - From Plants to Humans
While genetic engineering has been used extensively in agriculture, recent advancements in technology for editing DNA and genes have provided the opportunity for improvements in the treatment of disease. Like genetic engineering in plants, gene editing in humans involves using laboratory technologies to edit the DNA code that makes up our genes, which are like the instructions for how our bodies should function.
There are many diseases that can be caused by changes– or mutations– to our DNA code. A revolutionary biotechnology called CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) is a tool that has the ability to precisely cut a specific spot of DNA to edit the DNA code. This has created the ability for medicines that not only treat the symptoms of diseases caused by mutations in the DNA code, but can target the exact mutations in the DNA causing the disease.
One example of how CRISPR can be used to treat disease is in sickle cell disease. Sickle cell disease is caused by a mutation in the DNA that contains the instructions for a protein found in red blood cells, hemoglobin. Hemoglobin plays an important role in delivering oxygen to tissues in the body. There is currently a treatment approved by the FDA that uses CRISPR to edit blood stem cells of a patient with sickle cell disease to increase the production of a type of hemoglobin that supports oxygen delivery.

Fueling the world … with corn?
Industry is another area where biotechnology is used. As humankind created industrial processes–like power plants to produce electricity, or cars, ships, and airplanes to provide transportation–fuels were needed to power these processes. Historically, fossil fuels, like coal, have been used to provide the energy needed for electricity, transportation, and heating. However, these fuels are nonrenewable (they take millions of years to form and can eventually run out) and can harm the environment in many ways. For example, the drilling and mining that are necessary to acquire these fuels damage animal habitats, and then when the fuels are burned, large amounts of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, are released.
Biofuels are a biotechnology solution for powering industrial processes in a way that is less harmful for the environment. Biofuels are liquid fuels produced from biomass: natural material that comes from plants and animals. Examples of biomass include wood, corn, and algae. Unlike fossil fuels, biofuels are renewable (they can be replenished in a short period of time) and they produce less gas and harmful substances. Biofuels provide an opportunity for powering our planet in a safer, more sustainable way.

Conclusion
Biotechnology in plants, medicine, and fuel–these are just a few examples of how harnessing natural processes can benefit the world! Our current technology is not perfect though, and researchers face many barriers as they work on changing DNA to heal sickness or using corn to power cars. For example, while gene editing provides an opportunity to cure diseases, it also has the potential to cause harmful side effects and unintended changes to DNA. While corn may be utilized to create fuel, corn is also needed for food, so growing crops for biofuels has to be balanced with growing crops for feeding the world.
Despite these challenges, biotechnology has a bright future. Thanks to the perseverance of scientists tackling complex problems, ongoing research and innovation continue to make improvements and discover solutions. Thus, one thing is certain: biotechnology will continue to make a positive impact on our world.

Author: Caitlin Silva
When this answer was published in 2025, Caitlin was a student in the Human Genetics and Genetic Counseling master’s program at Stanford. Caitlin wrote this answer while participating in the Stanford at The Tech program.
 Skip Navigation
Skip Navigation
